What is Disk Storage?
Microsoft Azure Disk Storage is based on Page Blobs. A Virtual machine can have one or more data disks that are also stored as virtual hard disks (VHDs) stored in an Azure storage account. It allows data to be persistently stored and accessed from an attached virtual hard disk. Basically, its your local drive!
Different Types of Disks in Azure
There are two types of Disks in Azure: Managed Disk and Unmanaged Disk
Managed Disk
They are block-level storage volumes that are managed by Azure and used with Azure Virtual Machines. Managed disks are like a physical disk in an on-premises server but, virtualized. With managed disks, all you have to do is specify the disk size, the disk type, and provision the disk. Then, Azure handles the rest.
Unmanaged Disk
It is a traditional type of disk that has been used by VMs. We can create a Storage Account and then create the disk within that Storage Account. We are responsible for managing it , taking care of the maximum input/output operations per second (IOPS) limit. We must not put too many disks in the same storage account, resulting in the VMs being throttled.
Disk roles
There are three main disk roles in Azure: the data disk, the OS disk, and the temporary disk. These roles map to disks that are attached to your virtual machine.
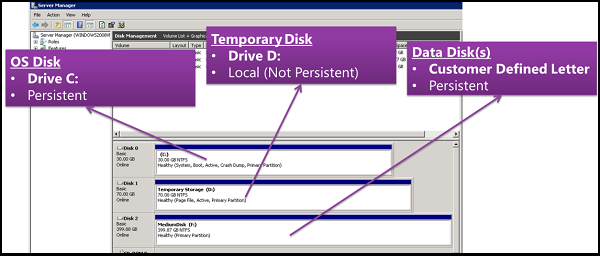
- Data disk: It is a managed disk that’s attached to a virtual machine to store application data, or other data you need to keep.
- OS disk: That OS disk has a pre-installed OS, which was selected when the VM was created. This disk contains the boot volume.
- Temporary disk: Most VMs contain a temporary disk, which is not a managed disk. They provides short-term storage for applications and processes, and is intended to only store data such as page or swap files.
Azure managed disk types
Azure managed disks currently offers five disk types. The following table provides a comparison of the five disk types to help you decide which to use.
| Ultra disk | Premium SSD v2 | Premium SSD | Standard SSD | Standard HDD | |
| Disk type | SSD | SSD | SSD | SSD | HDD |
| Scenario | IO-intensive workloads such as SAP HANA, top tier databases (Example. SQL, Oracle), and other transaction heavy workloads. | Production and performance sensitive workloads that consistently require low latency and high IOPS and throughput | Production and performance sensitive workloads | Web servers, lightly used enterprise applications and dev/test | Backup, non-critical, infrequent access |
| Max disk size | 65,536 GiB | 65,536 GiB | 32,767 GiB | 32,767 GiB | 32,767 GiB |
| Max throughput | 4,000 MB/s | 1,200 MB/s | 900 MB/s | 750 MB/s | 500 MB/s |
| Max IOPS | 160,000 | 80,000 | 20,000 | 6,000 | 2,000 |
| OS Disk? | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |